what functional groups are common to both of structures below?
Functional Groups
Functional Groups
Bromine reacts with two-butene to class 2,3-dibromobutane.
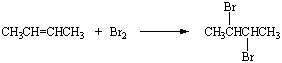
Information technology also reacts with three-methyl-ii-pentene to form 2,3-dibromopentane.

Instead of trying to memorize both equations, we can build a general rule that bromine reacts with compounds that contain a C=C double bond to give the product expected from addition across the double bond. This approach to agreement the chemistry of organic compounds presumes that sure atoms or groups of atoms known as functional groups give these compounds their feature properties.
Functional groups focus attending on the important aspects of the structure of a molecule. We don't take to worry well-nigh the differences betwixt the structures of 1-butene and 2-methyl-2-hexene, for example, when these compounds react with hydrogen bromide. We can focus on the fact that both compounds are alkenes that add together HBr across the C=C double bond in the direction predicted by Markovnikov's rule.

Some common functional groups are given in the table beneath.
Common Functional Groups
The C=O group plays a specially of import role in organic chemistry. This grouping is called a carbonyl and some of the functional groups based on a carbonyl are shown in the table below.
Functional Groups That Contain a Carbonyl
Root beer hasn't tasted the same since the use of sassafras oil equally a food additive was outlawed considering sassafras oil is lxxx% safrole, which has been shown to cause cancer in rats and mice. Identify the functional groups in the structure of safrole.

Click hither to check your answer to exercise problem 1
The following compounds are the active ingredients in over-the-counter drugs used every bit analgesics (to salvage hurting without decreasing sensibility or consciousness), antipyretics (to reduce the trunk temperature when it is elevated), and/or anti-inflammatory agents (to counteract swelling or inflammation of the joints, pare, and eyes). Identify the functional groups in each molecule.

Click here to check your reply to exercise problem 2
The discovery of penicillin in 1928 marked the starting time of what has been called the "golden age of chemotherapy," in which previously life-threatening bacterial infections were transformed into little more than a source of discomfort. For those who are allergic to penicillin, a variety of antibiotics, including tetracycline, are available. Identify the numerous functional groups in the tetracycline molecule.

Click here to check your reply to practice problem iii
![]()
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Focusing on the functional groups in a molecule allows us to recognize patterns in the behavior of related compounds. Consider what nosotros know about the reaction between sodium metal and water, for example.
2 Na(southward) + 2 HtwoO(fifty) ![]() Htwo(g) + two Na+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq)
Htwo(g) + two Na+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq)
We can divide this reaction into two half-reactions. Ane involves the oxidation of sodium metallic to form sodium ions.
| Oxidation: | Na | | Na+ + e- |
The other involves the reduction of an H+ ion in h2o to grade a neutral hydrogen atom that combines with some other hydrogen atom to form an Htwo molecule.
| Reduction: |  |
In one case we recognize that water contains an![]() OH functional group, we can predict what might happen when sodium metal reacts with an booze that contains the same functional grouping. Sodium metal should react with methanol (CHthreeOH), for example, to give Htwo gas and a solution of the Na+ and CHiiiO- ions dissolved in this alcohol.
OH functional group, we can predict what might happen when sodium metal reacts with an booze that contains the same functional grouping. Sodium metal should react with methanol (CHthreeOH), for example, to give Htwo gas and a solution of the Na+ and CHiiiO- ions dissolved in this alcohol.
2 Na(south) + 2 CH3OH(fifty) ![]() Htwo(g) + 2 Na+(alc) + ii CH3O-(alc)
Htwo(g) + 2 Na+(alc) + ii CH3O-(alc)
Considering they involve the transfer of electrons, the reaction between sodium metal and either water or an alcohol are examples of oxidation-reduction reactions. But what about the following reaction, in which hydrogen gas reacts with an alkene in the presence of a transition metal catalyst to form an alkane series?

There is no change in the number of valence electrons on whatsoever of the atoms in this reaction. Both before and after the reaction, each carbon cantlet shares a total of eight valence electrons and each hydrogen atom shares two electrons. Instead of electrons, this reaction involves the transfer of atoms![]() in this case, hydrogen atoms. There are and then many atom-transfer reactions that chemists developed the concept of oxidation number to extend the idea of oxidation and reduction to reactions in which electrons aren't necessarily gained or lost.
in this case, hydrogen atoms. There are and then many atom-transfer reactions that chemists developed the concept of oxidation number to extend the idea of oxidation and reduction to reactions in which electrons aren't necessarily gained or lost.
| Oxidation involves an increment in the oxidation number of an atom. |
| Reduction occurs when the oxidation number of an atom decreases. |
During the transformation of ethene into ethane, there is a decrease in the oxidation number of the carbon atom. This reaction therefore involves the reduction of ethene to ethane.

Reactions in which none of the atoms undergo a alter in oxidation number are called metathesis reactions. Consider the reaction betwixt a carboxylic acid and an amine, for example.
![]()
Or the reaction between an alcohol and hydrogen bromide.
![]()
These are metathesis reactions considering there is no change in the oxidation number of any atom in either reaction.
The oxidation numbers of the carbon atoms in a variety of compounds are given in the table below.
Typical Oxidation Numbers of Carbon
| Functional Group | Example | Oxidation Number of Carbon in the Case | ||
| Alkane series | CH4 | -4 | ||
| Alkyllithium | CHthreeLi | -four | ||
| Alkene | HiiC=CH2 | -2 | ||
| Alcohol | CH3OH | -2 | ||
| Ether | CH3OCH3 | -2 | ||
| Alkyl halide | CHthreeCl | -2 | ||
| Amine | CHthreeNH2 | -2 | ||
| Alkyne | HC | -1 | ||
| Aldehyde | H2CO | 0 | ||
| Carboxylic acid | HCOtwoH | two | ||
| CO2 | four |
These oxidation numbers can be used to allocate organic reactions equally either oxidation-reduction reactions or metathesis reactions.
Because electrons are neither created nor destroyed, oxidation tin can't occur in the absence of reduction, or vice versa. It is oft useful, still, to focus attention on 1 component of the reaction and ask: Is that substance oxidized or reduced?
Assigning oxidation numbers to the individual carbon atoms in a circuitous molecule can be difficult. Fortunately, there is another style to recognize oxidation-reduction reactions in organic chemistry:
Oxidation occurs when hydrogen atoms are removed from a carbon atom or when an oxygen atom is added to a carbon atom.
Reduction occurs when hydrogen atoms are added to a carbon atom or when an oxygen atom is removed from a carbon atom.
The get-go reaction in practice problem 5 involves oxidation of the carbon cantlet considering a pair of hydrogen atoms are removed from that cantlet when the alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde.
![]()
The second reaction in practice trouble five is an instance of oxidation considering an oxygen atom is added to the carbon atom when an aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid.
![]()
Reduction, on the other hand, occurs when hydrogen atoms are added to a carbon atom or when an oxygen atom is removed from a carbon atom. An alkene is reduced, for instance, when it reacts with H2 to form the corresponding alkane series.
![]()
The figure beneath provides a useful guide to the oxidation-reduction reactions of organic compounds. Each of the arrows in this figure involves a two-electron oxidation of a carbon atom along the path toward carbon dioxide. A line is fatigued through the starting time arrow considering it is impossible to achieve this transformation in a single step.

![]()
Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups
Functional Groups | Alkyl Halides | Alcohols and Ethers | Aldehydes and Ketones | The Carbonyl Group | Amines, Alkaloids, and Amides | Grignard Reagents
Research in the 1990's: The Chemistry of Garlic
Periodic Table | Glossary | Cool Applets
Gen Chem Topic Review | General Chemistry Assistance Homepage | Search: The general chemistry web site.
Source: https://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/2organic/function.html
0 Response to "what functional groups are common to both of structures below?"
Postar um comentário